food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome treatment
There is no role for the use of adrenaline epinephrine autoinjectors in the management of FPIES. Treatment during an FPIES reaction may include.

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table
Those treatments will help lessen the FPIES reaction but they wont treat the condition.

. There is currently no cure or treatment for FPIES. FPIES reactions can be. Avoidance of the trigger foods is the mainstay of treatment.
Milk and dairy products soy or soymilk and wheat or other grains are the most common foods that cause an attack. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines. The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet.
Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. In more severe cases Panchakarma therapy plays a vital role as it quickly detoxifies rejuvenates the digestive system. I-FPIES is a worldwide leader.
While seminal studies report that children may outgrow FPIES between ages 2 and 3 many. Individuals with FPIES experience profuse vomiting and diarrhea that usually. These symptoms can lead to severe lethargy change in body temperature and blood pressure.
If a severe reaction does occur treatment includes the administration of intravenous fluids to counteract fluid loss from vomiting and diarrhea. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a rare disorder mostly affecting infants 0-3 years and young children 3-10 years which occurs when foods that harm the gastrointestinal tract are taken. Some kids also can be allergic.
Treatment involves identifying and avoiding the food that causes the reaction. The preventive diet will only be implemented if at the time of the FPIES. Ayurvedic treatment of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome involves Shamana chikitsa internal medicines Shodana chikitsa Panchakarma therapy lifestyle modifications and a very strict diet regime.
Treatment for FPIES must be individualized and is often modified as the child grows. In the last years the interest of the scientific community toward food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES has grown exponentially. The best way to manage FPIES is to strictly avoid the food that triggers an allergic reaction.
We review here the peculiar characteristics of this syndrome. FPIES Treatment and Course. FPIES usually develops in infancy and resolves around 3-5 years of age.
The recent publication of the First International Consensus Guidelines allowed a positive interaction between different research groups with. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypothermia hypotension and metabolic derangements. Intravenous IV fluids because of the risk of dehydration.
FPIES food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome is a serious allergic reaction to certain foods. Adults and children have different experiences with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome although more research is necessary according to a study published in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. The principal suggested treatments are intravenous fluids and steroids whereas the use.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES is a delayed-type food allergic reaction in the gastrointestinal system which typically presents in the first year of life. In some cases a feeding tube is required. The treatment of FPIES includes infants being taken off offending foods and being exclusively breast fed or given an elemental medical formula.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. If your child has solid-food FPIES your allergist may suggest introducing fruits and vegetables pears bananas and potatoes for example rather than cereals and grains. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system.
This requires careful attention to your childs diet. Your doctor will advise as to how to alter the diet to achieve this and you may receive advice from a dietitian if the foods to be removed include a major food group. Most children outgrow FPIES by school age and regular visits to a treating physician are part of the treatment plan.
9 rows Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated. The only treatment for FPIES is to avoid the trigger food. The principal suggested treatments.
Any food can cause an FPIES reaction but the most common triggers are dairy and soy. FPIES is an alarming condition in which its patients may be diagnosed with failure to thrive although it is hardly. Avoidance of triggering foods ensuring good nutrition healing the gut balancing the immune system and maintaining a good inflammatory balance are keys to treatment.
The same is true for the breast-feeding mother if there is a clear connection between breast milk intake and the babys symptoms. Prevention and Management. It may be useful to give patients families an action plan.
FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is being increasingly recognized. In emergency situations the primary treatment for an FPIES episode is intravenous fluids for rehydration. The quality of life for patients and families affected by Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES by means of education research advocacy and support.
There is no specific treatment for. Or the stomach flu. Clinical management food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome oral food challenge INTRODUCTION The clinical management of a patient who has.
Steroid treatments may also be used to lessen an immune reaction. If your child has FPIES to milksoy formula your allergist may advise you switch to using a hypoallergenic formula such as a casein hydrolysate-based formula. First recurrence of acute FPIES episodes due to accidental ingestion of culprit food.
Corticosteroids and in-hospital monitoring for more severe symptoms. If your young infant has FPIES caused by a cows milk-based infant formula their pediatrician might also recommend avoiding soy formula given that infants with FPIES to. Specifically unlike what has been document in the pediatric population the adult cohort less frequently experienced vomiting.

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
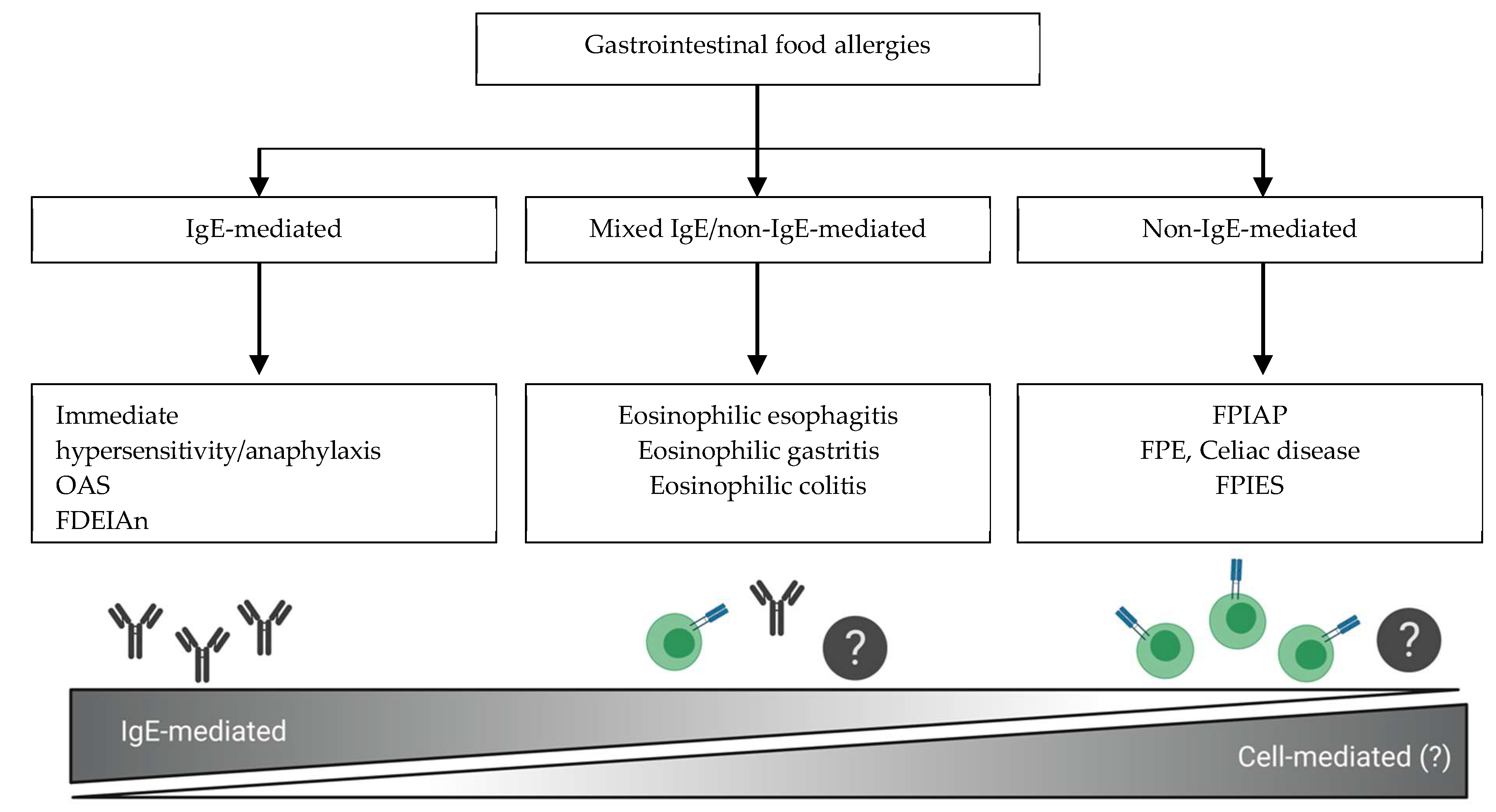
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

Tweets With Replies By Eastmidsfoamed Em3foamed Twitter

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Comparison Between Acute And Chronic Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram
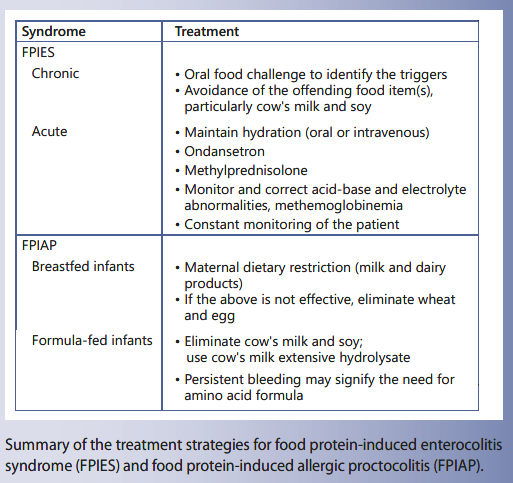
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Description Of Differences And Similarities Between Fpies Fpe And Download Scientific Diagram

Algorithm For The Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect